【Spring Boot】第9.4課-使用 JPA 配置資料表關聯(以一對一關聯為例)
本文最後更新於:2025-03-22
在上一篇,我們已經知道如何對單一資料表進行 CRUD,而本文將以「學生」與「聯繫方式」為情境,解說如何把兩張資料表關聯起來。並且也會撰寫 RESTful API,示範用法。
剛開始使用 JPA 進行配置時,會遇到許多新觀念。包含各種 annotation、加載策略、級聯,以及潛在的 N + 1 問題。本文會以最簡單的一對一關聯做為起點,往後學習其他關聯方式,將會更順利。
一、程式專案準備
(一)實體類別介紹
以下的「Student」類別,描述了學生資料,包含 id 與名字這 2 個欄位。
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
// getter, setter ...
}以下的「Contact」類別,描述了聯繫方式,包含信箱與電話這 2 個欄位。
@Entity
@Table(name = "contact")
public class Contact {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String email;
private String phone;
// getter, setter ...
}它們在資料庫中,都會有自己的資料表(table)。
(二)JPA Repository
上述的 Student 和 Contact 都是要儲存到資料庫的實體類別,因此需建立各自的 repository。
以下的「StudentRepository」宣告了一個方法,用來查詢 name 欄位包含某段字串的資料(不分大小寫)。
@Repository
public interface StudentRepository extends JpaRepository<Student, Long> {
List<Student> findByNameLikeIgnoreCase(String name);
}以下是「ContactRepository」,無自定義方法。
@Repository
public interface ContactRepository extends JpaRepository<Contact, Long> {
}(三)準備測試資料
啟動程式後,JPA 便會在資料庫中建立好 table。若讀者有需要,可執行以下 SQL 指令,產生測試資料。
INSERT INTO `student` (`name`)
VALUES ("Vincent"), ("Ivy"), ("Linda");
INSERT INTO `contact` (`email`, `phone`)
VALUES
("vincent@school.com", "0911"),
("ivy@school.com", "0922"),
("linda@school.com", "0933");
UPDATE `student`
SET `contact_id` = (SELECT `id` FROM `contact` WHERE `phone` = "0911")
WHERE `name` = "Vincent";
UPDATE `student`
SET `contact_id` = (SELECT `id` FROM `contact` WHERE `phone` = "0922")
WHERE `name` = "Ivy";
UPDATE `student`
SET `contact_id` = (SELECT `id` FROM `contact` WHERE `phone` = "0933")
WHERE `name` = "Linda";二、設計一對一關聯
(一)設計原則
所謂的一對一關聯,指的是其中一張 table 的 1 筆資料,只會對應到另一張 table 的 1 筆資料,反之亦然。
現在我們有「學生」與「聯繫方式」這兩張 table。在聯繫表中,有信箱和電話這 2 個欄位,每組資料都是屬於一位學生的。而每位學生都有對應的一組聯繫方式。
兩張 table 的關聯方式,是在其中一張 table 中添加額外的欄位做為外鍵(Foreign Key,FK),指向另一張 table 的主鍵(Primary Key,PK)。此時有兩種選擇:
- 在學生表添加 FK 欄位,指向聯繫表的 PK。強調每位學生擁有一組聯繫方式。
- 在聯繫表添加 FK 欄位,指向學生表的 PK。強調每組聯繫方式都有它的擁有者。
那麼要在哪一張 table 添加 FK 欄位呢?原則上會選擇商業邏輯中,更重要的 table,也就是學生表,因為聯繫方式是學生資料的一部份。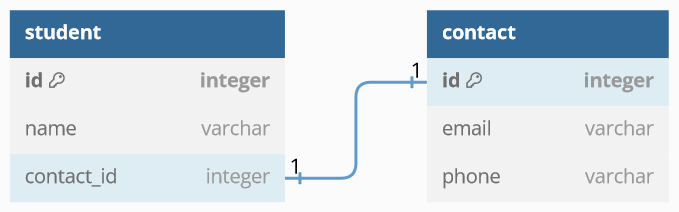
(二)程式配置
回到程式專案,以下是在 Student 實體類別配置一對一關聯。
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
// ...
@OneToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "contact_id", referencedColumnName = "id", nullable = false, unique = true)
private Contact contact;
// getter, setter ...
}此處在實體類別添加了 Contact 欄位,並冠上 @OneToOne 注解,表明一對一關聯。
這個 Contact 欄位會以 FK 欄位的形式儲存在 table 中。為此,需使用 @JoinColumn 注解來取名。在 name 參數可傳入欄位名稱;而 referencedColumnName 參數,則定義該欄位要關聯到聯繫表的 id 欄位,也就是 PK。
若聯繫方式為必填資料,那麼可在 nullable 參數傳入 false,將 FK 設成「NOT NULL」。另外,聯繫方式是每位學生自己專屬的,不會與人共用,因此設為 unique。
當呼叫 StudentRepository 進行查詢時,每筆學生資料所關聯到的聯繫方式,會被載入到 Contact 欄位中,讓我們在程式碼中運用。
(三)測試用 API
為了確認一對一關聯的效果,我們會在 Controller 設計 RESTful API,透過 repository 存取資料庫。
以下提供了一支 API,用途是透過學生名字的關鍵字來查詢。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@GetMapping("/students")
public ResponseEntity<List<StudentResponse>> getStudents(
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "") String name
) {
List<Student> students = studentRepository.findByNameLikeIgnoreCase("%" + name + "%");
List<StudentResponse> responses = students
.stream()
.map(s -> {
Contact c = s.getContact();
StudentResponse res = new StudentResponse();
res.setId(s.getId());
res.setName(s.getName());
res.setEmail(c.getEmail());
res.setPhone(c.getPhone());
return res;
})
.toList();
return ResponseEntity.ok(responses);
}
}邏輯上是先呼叫 repository 查詢資料,接著將結果包裝成如下的 response body。
public class StudentResponse {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String phone;
// getter, setter ...
}在進行包裝的過程中,會從 Student 實體取出 Contact 物件。要注意的是,該物件實際上是 Hibernate 的「代理物件」(proxy),本身並不支援在 API 回傳時,被序列化成 JSON,所以此處才要另外取出欄位值。
三、加載策略
上一節最後有提到,查詢到的 Student 實體,其所關聯的 Contact 實體,是 Hibernate 的「代理物件」。我們可設定「加載策略」,控制在查詢 Student 時,是否要馬上將關聯的 Contact 一起查詢回來。
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
// ...
@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "contact_id", referencedColumnName = "id", nullable = false, unique = true)
private Contact contact;
// getter, setter ...
}此處在 @OneToOne 注解傳入了 fetch 參數。FetchType.EAGER 代表立即查詢回來,同時也是 @OneToOne 注解的預設值。而 FetchType.LAZY 代表需要用到時,才會進行查詢。
為了觀察兩者的差別,請讀者在 application.properties 配置檔添加以下 2 個設定值。用途是讓 JPA 存取資料庫時,將執行的 SQL 指令印在 console 中,並做排版。
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.show_sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true在上一節的 API 中,首先呼叫了 StudentRepository。假設加載策略設為 FetchType.EAGER,且查詢到的學生資料有 2 筆,那 JPA 會「立即」印出類似下面的內容:
Hibernate:
SELECT s.id, s.name, s.contact_id
FROM student s
WHERE UPPER (s.name) LIKE UPPER (?)
Hibernate:
SELECT c.id, c.email, c.phone
FROM contact c
WHERE c.id = ?
Hibernate:
SELECT c.id, c.email, c.phone
FROM contact c
WHERE c.id = ?第一條指令是查詢所有學生資料,並取得 FK,也就是「contact_id」欄位的值。第二、三條指令則是分別查詢聯繫表,將 Contact 實體加載到兩個 Student 實體中。
若加載策略設為 FetchType.LAZY,則需等到呼叫「getContact()」方法取得關聯的實體時,JPA 才會實際查詢聯繫表。
特別的是,若直接以「getContact().getId()」的方式連續呼叫,是不會引發查詢的。相對地,只會取得學生表的 FK 欄位值。
四、認識 N + 1 問題
所謂的 N + 1 問題,大方向可以解釋成:一開始查詢到了 N 個資料實體(如 Student)。但它們所關聯的次要實體(如 Contact),是「一個一個」地分別查詢出來,於是又查詢了 N 次,形成對資料庫的大量存取。
這可能會在什麼情況發生呢?其實在第三節的例子中,我們就可以觀察到了。假設將加載策略設為 FetchType.EAGER,且又查詢出多筆 Student 資料,那 JPA 就會馬上逐一查詢他們的 Contact 資料。
又或者是將加載策略設為 FetchType.LAZY,且我們呼叫 Student 的「getContact()」方法,逐一取出所有 Contact 實體,那也會引發多次對資料庫的查詢,造成 N + 1 問題。
這裡提供一個解決的方式。首先選擇 FetchType.LAZY 做為加載策略,接著將取得 Contact 實體的做法,調整為用「IN」的方式一次查詢。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@Autowired
private ContactRepository contactRepository;
@GetMapping("/students")
public ResponseEntity<List<StudentResponse>> getStudents(
@RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "") String name
) {
List<Student> students = studentRepository.findByNameLikeIgnoreCase("%" + name + "%");
// 建立 Student 與 Contact 的對應關係
Map<Student, Contact> studentContactMap = createStudentContactMap(students);
List<StudentResponse> responses = students
.stream()
.map(s -> {
Contact contact = studentContactMap.get(s);
StudentResponse res = new StudentResponse();
res.setId(s.getId());
res.setName(s.getName());
res.setEmail(contact.getEmail());
res.setPhone(contact.getPhone());
return res;
})
.toList();
return ResponseEntity.ok(responses);
}
private Map<Student, Contact> createStudentContactMap(List<Student> students) {
// Student 對應 FK (contact id)
Map<Student, Long> studentContactIdMap = students
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Function.identity(), s -> s.getContact().getId()));
// PK (contact id) 對應 Contact
List<Contact> contacts = contactRepository.findAllById(studentContactIdMap.values());
Map<Long, Contact> contactMap = contacts
.stream()
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Contact::getId, Function.identity()));
Map<Student, Contact> map = new HashMap<>();
students.forEach(s -> {
Long contactId = studentContactIdMap.get(s);
Contact contact = contactMap.get(contactId);
map.put(s, contact);
});
return map;
}
}以上的範例程式,會在查詢到學生後,將學生與 FK 的值整理成 Map 結構。即便加載策略為 FetchType.LAZY,但以「Student.getContact().getId()」的形式連續呼叫,並不會引發額外的查詢。
接著將學生的 FK,也就是聯繫方式的 PK,傳入 ContactRepository 的 findAllById 方法,一次查詢出所有 Contact 實體。最後將 PK 與實體也整理成 Map 結構。
如此一來,我們便可在程式碼的層級,將兩種實體關聯起來了。重新存取 API 後,在 console 印出的 SQL 指令,示意如下:
Hibernate:
SELECT s.id, s.name, s.contact_id
FROM student s
WHERE UPPER (s.name) LIKE UPPER (?)
Hibernate:
SELECT c.id, c.email, c.phone
FROM contact c
WHERE c.id IN (?, ?)可看出只對資料庫進行 2 次查詢而已。第一個指令是查詢學生資料,在此假設查到 2 筆。而第二個指令的 WHERE 子句出現了「IN」關鍵字,且有 2 個問號,代表 JPA 是透過這 2 位學生的 FK,一次查詢所有聯繫資料。
五、級聯(Cascade)
(一)前言
在目前的設計中,Student 實體持有了 Contact 實體,而學生表也有 FK 欄位去指向聯繫表的 PK 欄位。此時我們稱學生表為關聯的「維護方」,而聯繫表為「被維護方」。
JPA 提供一種叫做「級聯」的機制,它讓我們在插入、更新或刪除維護方所關聯的實體物件時,能自動同步到被維護方。
@Entity
@Table(name = "student")
public class Student {
// ...
@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.REMOVE})
@JoinColumn(name = "contact_id", referencedColumnName = "id", nullable = false, unique = true)
private Contact contact;
// ...
}在 @OneToOne 的 cascade 參數,可設定哪些操作需要對被維護方的實體套用級聯。CascadeType.PERSIST 代表呼叫 repository 的 save 方法,插入或更新維護方的實體時會生效。CascadeType.REMOVE 代表刪除維護方的實體時會生效。
(二)級聯插入
以下是在 Controller 提供建立學生資料的 API。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@PostMapping("/students")
public ResponseEntity<Void> createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
student.setId(null);
studentRepository.save(student);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}範例程式中,雖然只有將 Student 物件傳入 StudentRepository 的 save 方法進行儲存,但 JPA 也會自動在聯繫表插入其內部 Contact 物件的資料。
JPA 在 console 印出的指令內容,示意如下。可看到會先插入聯繫資料,再插入學生資料,並填入 FK 欄位的值。
Hibernate:
INSERT INTO contact (email, phone)
VALUES (?, ?)
Hibernate:
INSERT INTO student (name, contact_id)
VALUES (?, ?)(三)級聯刪除
以下的 API 是刪除學生資料。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@DeleteMapping("/students/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Void> deleteStudent(@PathVariable Long id) {
studentRepository.deleteById(id);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}JPA 在 console 印出的指令內容,示意如下:
Hibernate:
SELECT s.id, s.name, s.contact_id
FROM student s
WHERE s.id = ?
Hibernate:
DELETE FROM student
WHERE id = ?
Hibernate:
DELETE FROM contact
WHERE id= ?可看到第一步是根據學生 id 查詢資料,藉此取得 FK 的值,也就是聯繫表的 PK。接著在刪除過程中,會先刪除學生,才刪除聯繫方式,避免 FK 關聯不到 PK(違反約束)。
(四)級聯更新
以下的 API 是單獨更新學生的聯繫方式。
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private StudentRepository studentRepository;
@PutMapping("/students/{id}/contact")
public ResponseEntity<Void> updateStudentContact(
@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Contact request
) {
Optional<Student> studentOp = studentRepository.findById(id);
if (studentOp.isEmpty()) {
return ResponseEntity.notFound().build();
}
Student student = studentOp.get();
Contact contact = student.getContact();
contact.setEmail(request.getEmail());
contact.setPhone(request.getPhone());
studentRepository.save(student);
return ResponseEntity.noContent().build();
}
}範例程式中,在查詢出學生資料後,隨即取出關聯的 Contact 實體。由於它是 Hibernate 的代理物件,為了不影響級聯的運作,因此實作上是將 request body 的內容更新上去,而不是呼叫「setContact」方法,直接覆蓋掉 Student 實體的 Contact 內容。
JPA 在 console 印出的指令內容,示意如下:
Hibernate:
SELECT s.id, s.name, s.contact_id
FROM student s
WHERE s.id = ?
Hibernate:
SELECT c.id, c.email, c.phone
FROM contact c
WHERE c.id = ?
Hibernate:
UPDATE contact
SET email = ?,
phone = ?
WHERE id = ?可看到第一步是查詢學生資料。接著由於呼叫「getContact()」方法的緣故,又引發了對聯繫表的查詢。最後儲存 Student 實體時,才級聯更新 Contact。
本文的完成後專案,請點我。